Consider Rogaine (minoxidil) a topical treatment option, but understand its efficacy for alopecia areata varies. It’s generally more effective for managing hair loss in androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness), not alopecia areata’s unpredictable nature. While some individuals experience regrowth, results are inconsistent.
Minoxidil works by widening blood vessels in the scalp, potentially stimulating hair follicle activity. For alopecia areata, this mechanism might promote regrowth in affected areas. However, the patchy, unpredictable nature of the condition makes consistent results less likely than with other hair loss types. Expect gradual growth, if any, and be prepared for periods of no noticeable change.
Important Note: Always consult a dermatologist before using Rogaine, or any other treatment, for alopecia areata. They can assess your specific condition, rule out other underlying issues, and help determine the best course of action. They might recommend Rogaine alongside other treatments like corticosteroids or immunotherapy, for a more comprehensive approach. Your dermatologist can also monitor treatment progress and make adjustments as needed.
Remember: Alopecia areata treatment often requires patience and persistence. Don’t expect immediate or dramatic results. Consistent application of Rogaine, as directed by your doctor, is key. Managing expectations and maintaining open communication with your dermatologist will contribute significantly to a successful treatment plan.
- Rogaine for Alopecia Areata: A Detailed Look
- What is Alopecia Areata?
- How Rogaine (Minoxidil) Works
- Understanding the Follicle Cycle
- How to Use Rogaine Effectively
- Potential Side Effects
- Factors Influencing Results
- Rogaine’s Effectiveness in Alopecia Areata
- Factors Influencing Results
- Clinical Trial Data
- Alternative Treatments
- Consultation is Key
- Applying Rogaine for Alopecia Areata
- Potential Side Effects of Rogaine
- Less Common Side Effects
- Rogaine vs. Other Alopecia Areata Treatments
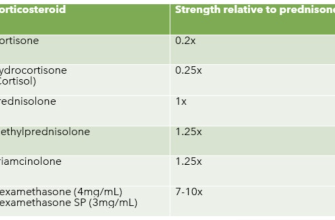
- Steroid Injections and Topical Corticosteroids
- Other Treatments
- When to Consult a Dermatologist
- Realistic Expectations and Treatment Duration
- Cost and Availability of Rogaine
- Where to Buy Rogaine
- Factors Affecting Cost
- Tips for Saving Money
Rogaine for Alopecia Areata: A Detailed Look
Rogaine, or minoxidil, is a topical medication approved by the FDA for androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern hair loss). While not explicitly approved for alopecia areata, many dermatologists prescribe it off-label due to its potential to stimulate hair growth.
Minoxidil works by widening blood vessels in the scalp, increasing blood flow to hair follicles. This enhanced circulation may promote hair growth in some individuals with alopecia areata. However, its effectiveness varies significantly. Some patients experience noticeable regrowth, while others see minimal or no improvement.
Typically, Rogaine is applied twice daily to the affected areas of the scalp. Consistent application is key; missed doses can hinder results. You should expect to use Rogaine for several months before observing any potential regrowth. Stopping treatment usually leads to hair loss resuming.
Before starting Rogaine, consult your dermatologist. They can assess your specific condition, discuss potential side effects (like scalp irritation or unwanted hair growth elsewhere), and determine if minoxidil is a suitable treatment option for you. They can also advise on other therapies, such as corticosteroids or immunotherapy, which might be more appropriate for your individual case.
Remember, alopecia areata’s treatment depends on the severity and type of hair loss. Rogaine might be part of a broader treatment plan. Individual responses to Rogaine vary greatly, and results aren’t guaranteed.
Side effects are possible and should be discussed with your healthcare provider. Be prepared to monitor your scalp closely for any unexpected reactions.
What is Alopecia Areata?
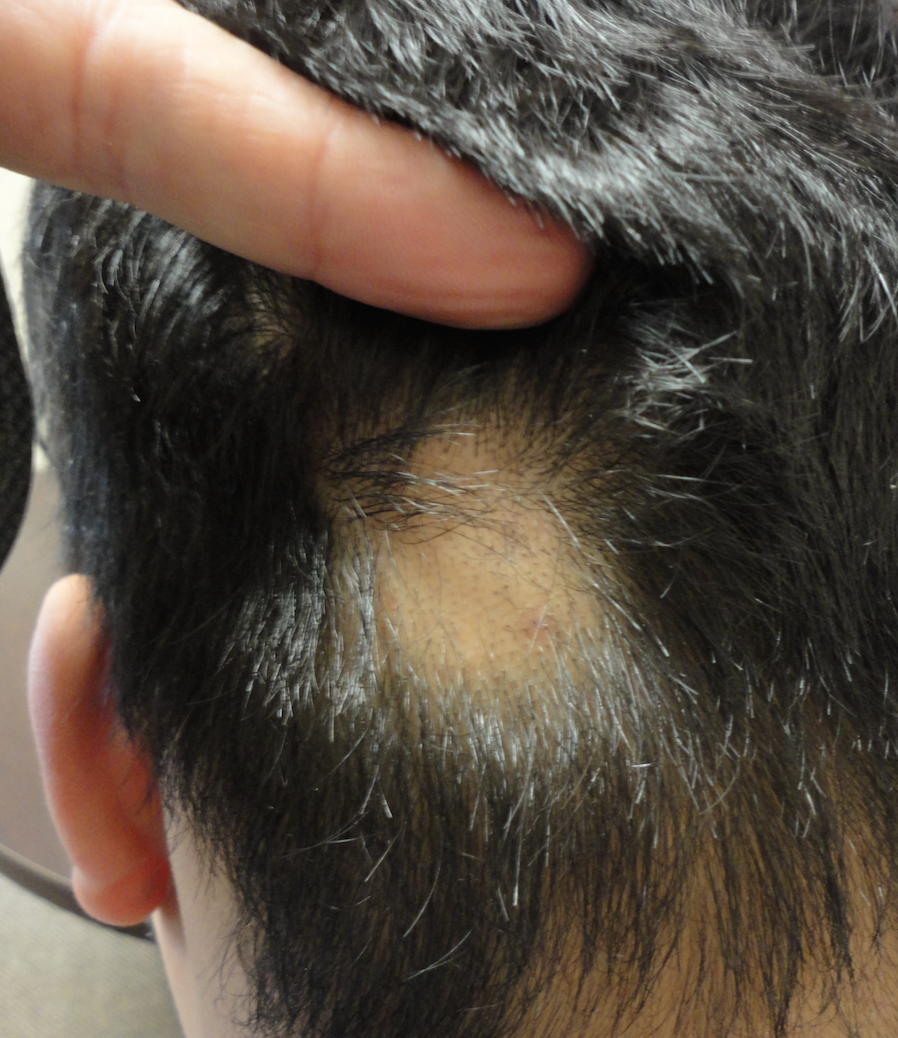
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing hair loss. Your immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss on the scalp, beard, or anywhere on the body. The condition affects people of all ages and genders, though it most often begins in childhood or adolescence.
Symptoms vary greatly. Some experience small, coin-sized bald patches, while others lose significant amounts of hair. In some cases, complete hair loss (alopecia totalis) or loss across the entire body (alopecia universalis) can occur. Hair may regrow spontaneously, or it might require treatment.
Diagnosis usually involves a physical examination by a dermatologist or doctor. They’ll review your medical history and assess the hair loss pattern. Biopsy may be used to rule out other causes.
Treatment options depend on the severity and location of hair loss, and your overall health. These can include topical corticosteroids, injections, light therapy, or oral medications. Rogaine (minoxidil), a topical medication, is sometimes used to encourage hair regrowth. Each treatment approach has different success rates and potential side effects, so consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Alopecia areata’s cause isn’t fully understood, but it’s believed to be linked to genetics and environmental factors. While a cure doesn’t currently exist, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve the chance of hair regrowth.
How Rogaine (Minoxidil) Works
Rogaine, containing minoxidil, primarily stimulates hair growth by widening blood vessels in the scalp. This increased blood flow delivers more oxygen and nutrients to hair follicles, promoting growth.
Understanding the Follicle Cycle
Minoxidil also influences the hair growth cycle. It prolongs the anagen phase (the growth phase), allowing hairs to grow longer before entering the telogen phase (resting phase) and ultimately shedding. This leads to thicker, fuller-looking hair over time.
How to Use Rogaine Effectively
- Follow the instructions on your specific Rogaine product carefully. Dosage and application methods vary.
- Apply the solution directly to the scalp, massaging gently to ensure even distribution. Do not apply to broken skin.
- Be patient. Results usually appear gradually, often after several months of consistent use. Consistency is key!
- Maintain regular use. Stopping treatment may result in hair loss.
Potential Side Effects
- Scalp irritation
- Hair growth in unwanted areas (if applied carelessly)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness (rare)
Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication, including Rogaine, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Factors Influencing Results
Individual responses to minoxidil vary. Factors such as the type and severity of alopecia areata, overall health, and genetics all play a role in treatment success.
Rogaine’s Effectiveness in Alopecia Areata
Rogaine (minoxidil), while approved for androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness), shows limited success in treating alopecia areata. Studies suggest a modest improvement in hair regrowth in some individuals, but results are highly variable.
Factors Influencing Results
Response to Rogaine varies considerably depending on factors such as the severity and extent of hair loss, the individual’s age and overall health, and the duration of alopecia areata. Some patients experience noticeable regrowth, while others see little to no change.
Clinical Trial Data
Several studies have investigated minoxidil’s use in alopecia areata. Results aren’t uniformly positive. While some small studies showed positive effects, larger, more rigorous trials often yield less impressive outcomes. Consult your dermatologist for the most current research data relevant to your case.
| Study | Sample Size | Regrowth Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study A | 100 | 25% | Significant improvement observed in a subset of patients. |
| Study B | 200 | 10% | Minimal regrowth noted; many experienced no change. |
| Study C | 50 | 30% | Higher regrowth rate; further research needed to replicate findings. |
Alternative Treatments
Alopecia areata often requires a multi-pronged approach. Besides Rogaine, your dermatologist might recommend other treatments like corticosteroids, immunotherapy, or JAK inhibitors, depending on the severity of your condition and your individual needs. Discuss all treatment options with your doctor to determine the best course of action for you.
Consultation is Key
Before using Rogaine for alopecia areata, it is crucial to consult a dermatologist. They can accurately diagnose your condition, assess the potential benefits and risks of using Rogaine, and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Applying Rogaine for Alopecia Areata
Use the correct formulation: Rogaine comes in 2% and 5% minoxidil strengths. Your doctor will determine the best option for you. 5% is generally recommended for scalp alopecia areata, but always follow your doctor’s advice.
Apply twice daily: Apply a consistent amount to the affected area. Don’t overuse; more isn’t better. Follow the instructions on the packaging regarding the quantity to use.
Cleanse your scalp: Wash and thoroughly dry your scalp before each application for optimal absorption. Avoid using heavily scented products or oils before application.
Be patient: Results take time. You may see improvement in hair regrowth after several months of consistent use. Remain diligent with the application schedule.
Monitor for side effects: Although generally safe, some experience scalp irritation or unwanted hair growth elsewhere. Discontinue use and consult your doctor if you experience adverse reactions.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Wash and dry your scalp |
| 2 | Measure the prescribed amount |
| 3 | Apply to the affected area(s) |
| 4 | Allow to dry completely |
| 5 | Repeat in the evening |
Consult your dermatologist: Regular checkups are important to monitor your progress and adjust treatment as needed. They can offer personalized advice and address any concerns.
Potential Side Effects of Rogaine
Rogaine, while often effective, can cause some side effects. These are usually mild and temporary, but it’s vital to be aware of them. The most common side effects include scalp irritation, such as redness, itching, or burning. This typically resolves as your body adjusts to the medication. Some individuals experience hair growth in unwanted areas, particularly on the face. This is more likely with the foam formulation.
Less Common Side Effects
Less frequently, users report headaches, dizziness, or rapid heartbeat. These are less common but should be reported to your doctor if they occur. Also, be mindful that Rogaine is for external use only. Avoid getting it in your eyes, nose, or mouth. Accidental ingestion can cause nausea or vomiting. If you experience any unexpected or concerning symptoms, discontinue use and consult your healthcare provider immediately. They can help determine if Rogaine is right for you and monitor for any potential complications.
Rogaine vs. Other Alopecia Areata Treatments
Rogaine (minoxidil) is a topical medication primarily used for androgenetic alopecia, but some find it helpful for certain alopecia areata cases, particularly mild ones. However, it’s not a first-line treatment for alopecia areata. More effective options exist.
Steroid Injections and Topical Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, administered via injection directly into affected patches or applied topically as creams or ointments, often represent a better initial approach. They effectively reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth in many alopecia areata patients. Expect quicker results compared to minoxidil, though effects can be temporary.
Other Treatments
Beyond corticosteroids, several other treatments show promise. Topical immunotherapy, like diphenylcyclopropenone (DPCP) or squaric acid dibutylester (SADBE), triggers an immune response that can stimulate hair regrowth. Oral medications, such as Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, are also emerging as powerful options for moderate to severe alopecia areata, though potential side effects need careful consideration and monitoring by a dermatologist.
Your dermatologist will determine the best course of action based on your specific condition, severity, and overall health. Factors like the size and number of affected patches, your age, and other medical conditions influence the treatment recommendation. Consult a specialist for personalized advice and to discuss potential risks and benefits of each therapy.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
Schedule a dermatologist appointment if Rogaine doesn’t show improvement after 4 months of consistent use. This timeframe allows for adequate assessment of the treatment’s efficacy.
Seek immediate professional help if you experience new or worsening symptoms, such as rapid hair loss, inflammation, or significant scalp irritation. These could indicate a change in your condition requiring immediate attention.
Consult your dermatologist if you notice any unusual side effects from using Rogaine, such as skin redness, burning, or itching that persists or intensifies. Accurate reporting helps ensure safe and appropriate treatment.
If your alopecia areata is widespread or severely impacting your quality of life, a dermatologist can discuss additional treatment options, beyond Rogaine, to manage your condition. They can offer personalized advice and a tailored treatment plan.
Don’t hesitate to contact a dermatologist if you have any questions or concerns about using Rogaine or managing your alopecia areata. Open communication ensures successful management of your hair loss.
Remember: Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes. Proactive communication with your dermatologist is key for successful treatment.
Realistic Expectations and Treatment Duration
Rogaine (minoxidil) can help some individuals with alopecia areata, but it’s not a guaranteed cure. Success varies greatly depending on factors like the extent and type of hair loss, individual response to the medication, and consistency of application.
Expect to use Rogaine for at least several months before noticing any potential regrowth. Many see results within 4-6 months, but others may take longer. Consistent application is key; skipping doses significantly reduces chances of success.
- Moderate Alopecia Areata: You might see some hair regrowth, but complete restoration is less likely. Treatment may need to continue indefinitely to maintain regrowth.
- Severe Alopecia Areata: Rogaine alone may prove insufficient. Consider it as part of a comprehensive treatment plan alongside other therapies, such as corticosteroids or immunotherapy.
- Early Alopecia Areata (small patches): This offers the highest potential for successful regrowth with minoxidil alone. However, hair loss may return if you discontinue treatment.
Here’s a realistic timeline to consider:
- Months 1-3: Minimal to no visible changes are common. Maintain consistent application.
- Months 4-6: Some individuals begin to see subtle hair regrowth. Be patient; results may be gradual.
- Months 6-12: Optimal regrowth often occurs within this timeframe. However, continued treatment is necessary to sustain results.
- Beyond 12 Months: Assess progress with your dermatologist. They may recommend adjusting the treatment plan or adding other therapies if regrowth plateaus or hair loss recurs.
Regular check-ups with your dermatologist are crucial for monitoring progress, adjusting dosage, or exploring alternative options if needed. Open communication with your doctor ensures you receive the best possible care and manage your expectations effectively.
Cost and Availability of Rogaine
Rogaine’s price varies depending on the formulation (foam or solution), concentration (2% or 5%), and quantity. Expect to pay between $30 and $70 per month for a typical supply. Generic minoxidil, the active ingredient in Rogaine, is generally cheaper.
Where to Buy Rogaine
- Pharmacies: Most major pharmacies (CVS, Walgreens, Walmart) stock Rogaine. Check their websites or apps for current prices and availability before visiting.
- Online Retailers: Amazon, Target, and other online retailers sell Rogaine. Compare prices across different sellers to find the best deal. Ensure you’re buying from a reputable source to avoid counterfeit products.
- Doctor’s Office: Your dermatologist may be able to provide a prescription for Rogaine or a generic alternative. This might offer a slightly different price point.
Factors Affecting Cost
- Concentration: 5% minoxidil is usually more expensive than 2% minoxidil.
- Formulation: Foam and solution may have slightly different prices.
- Quantity: Larger bottles generally cost less per ounce.
- Insurance Coverage: Check with your insurance provider to see if Rogaine or minoxidil is covered under your plan. This can significantly reduce your out-of-pocket cost.
Tips for Saving Money
- Buy in bulk: Purchasing larger quantities can lower the per-unit cost.
- Use coupons and discounts: Pharmacies and online retailers often offer coupons or discounts on Rogaine.
- Consider generic brands: Generic minoxidil is typically less expensive than name-brand Rogaine and provides the same active ingredient.
Remember to consult your doctor before starting any new hair loss treatment, including Rogaine.